Kia Optima DL3: Ignition System / Ignition Coil
Description and operation
| Description |
An ignition coil is an induction coil in an engine's ignition system which transforms the battery's low voltage to the high voltage needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs to ignite the fuel. Coils have an internal resistor while others rely on a resistor wire or an external resistor to limit the current flowing into the coil from the battery 12 V supply.
Specifications
| Specification |
|
Item |
Specification |
|
Primary Coil Resistance (Ω) |
0.75 ± 15% [20°C (68°F)] |
|
Secondary Coil Resistance (kΩ) |
5.9 ± 15% [20°C (68°F)] |
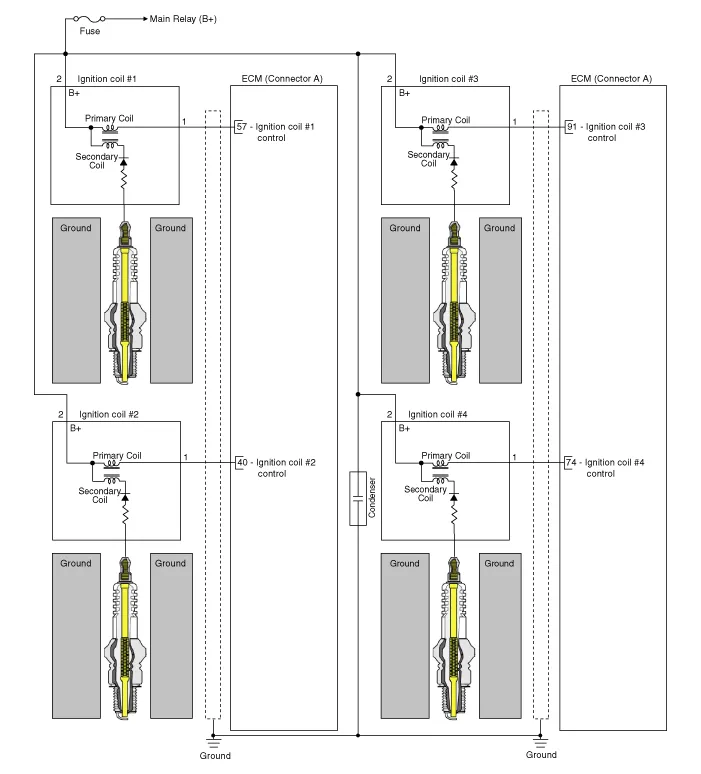
Schematic diagrams
| Circuit Diagram |
Repair procedures
| Removal |
| 1. |
Disconnect the negative battery (-) terminal. |
| 2. |
Remove the engine cover. |
| 3. |
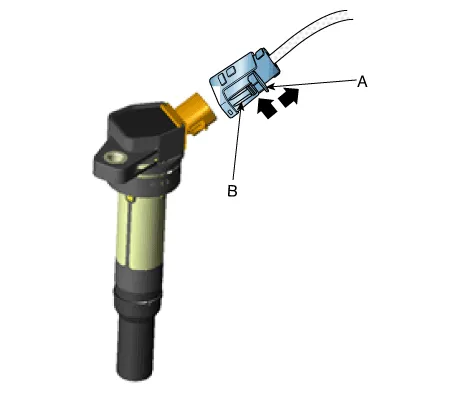
Disconnect the ignition coil connector (A).
|
| 4. |
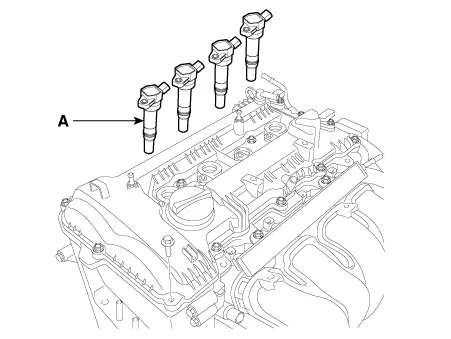
Remove the ignition coil (A).
|
| Installation |
| 1. |
Install in the reverse order of removal. |
| Inspection |
| 1. |
Measure the primary coil resistance between terminals 1 and 2.
|
Description and operation Description Ignition timing is controlled by the electronic control ignition timing system. The standard reference ignition timing data for the engine operating conditions are pre-pro grammed in the memory of the ECM (Engine Control Module).
Description and operation Description A spark plug is a device for delivering electric current from an ignition system to the combustion chamber of a spark-ignition engine to ignite the compressed fuel/air mixture therein by means of an electric spark, while containing combustion pressure within the engine.
Other information:
Kia Optima DL3 2019-2025 Service and Repair Manual: Power Window Motor
Schematic diagrams Circuit Diagram [Safety Window Motor] [Standard Window Motor] Repair procedures Inspection Front Power Window Motor 1. Disconnect the negative battery terminal. 2.
Kia Optima DL3 2019-2025 Service and Repair Manual: Compressor oil
Repair procedures Oil Specification 1. The HFC-134a system requires synthetic (PAG) compressor oil whereas the R-12 system requires mineral compressor oil. The two oils must never be mixed. 2. Compressor (PAG) oil varies according to compressor model.
Categories
- Manuals Home
- Kia Optima Owners Manual
- Kia Optima Service Manual
- Engine Mechanical System
- Body (Interior and Exterior)
- Engine Control / Fuel System
- New on site
- Most important about car